Ten reasons for growing and drinking Australian Coffee
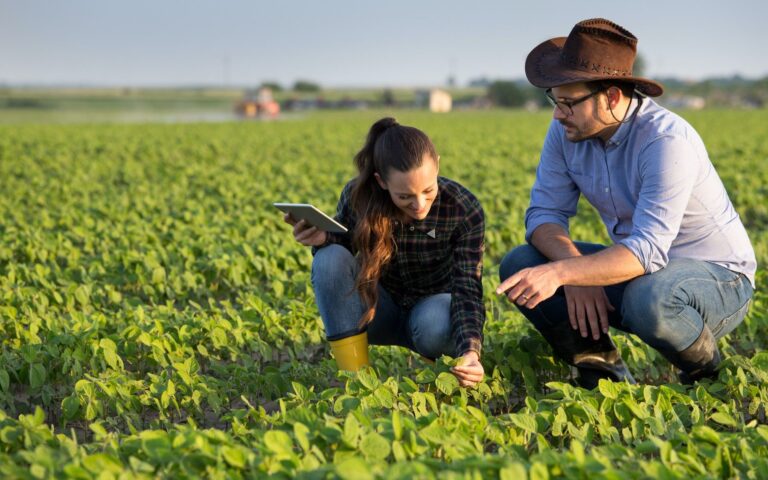
Could you be our next Australian coffee investor or producer? The cooler climate of Australia’s subtropical latitudes provides a longer ripening season which brings out...

The latest report from the Community Trust in Rural Industries program is now live.
Find out more
Ten reasons for growing and drinking Australian Coffee
Could you be our next Australian coffee investor or producer? The cooler climate of Australia’s subtropical latitudes provides a longer ripening season which brings out...
AgriFutures Tea Tree Oil Program RD&E Snapshot
Message from the Research Manager, Stephen Taylor As we head into a new research, development and extension (RD&E) period for the AgriFutures Tea Tree Oil...
Cultivating futures: Engaging secondary school students in the world of agricultural careers
Without an engaged, motivated and highly skilled future workforce, the agriculture industry will struggle to reach the National Farmers’ Federation’s aspirational target of being a...New research investigates the terroir of Australian grown coffee.
Find out moreFarmers interested in growing the crop are invited to inspect the sites at a series of field days planned for 2024.
Register nowA $2 million commitment fuelling 15 pioneering research projects.
Read moreListen to the latest AgriFutures On Air podcast episodes.
Listen now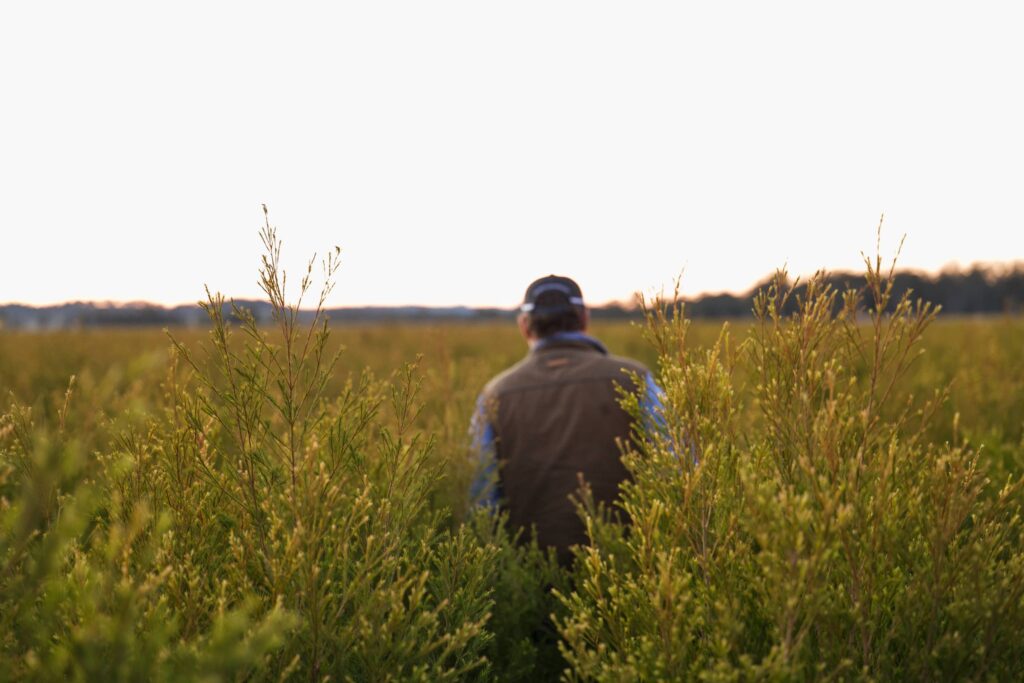
The AgriFutures Tea Tree Oil extension program is excited to partner with tea tree growers and industry stakeholders to bring you the 2024 Knowledge to Know-how Forum in Casino, NSW.
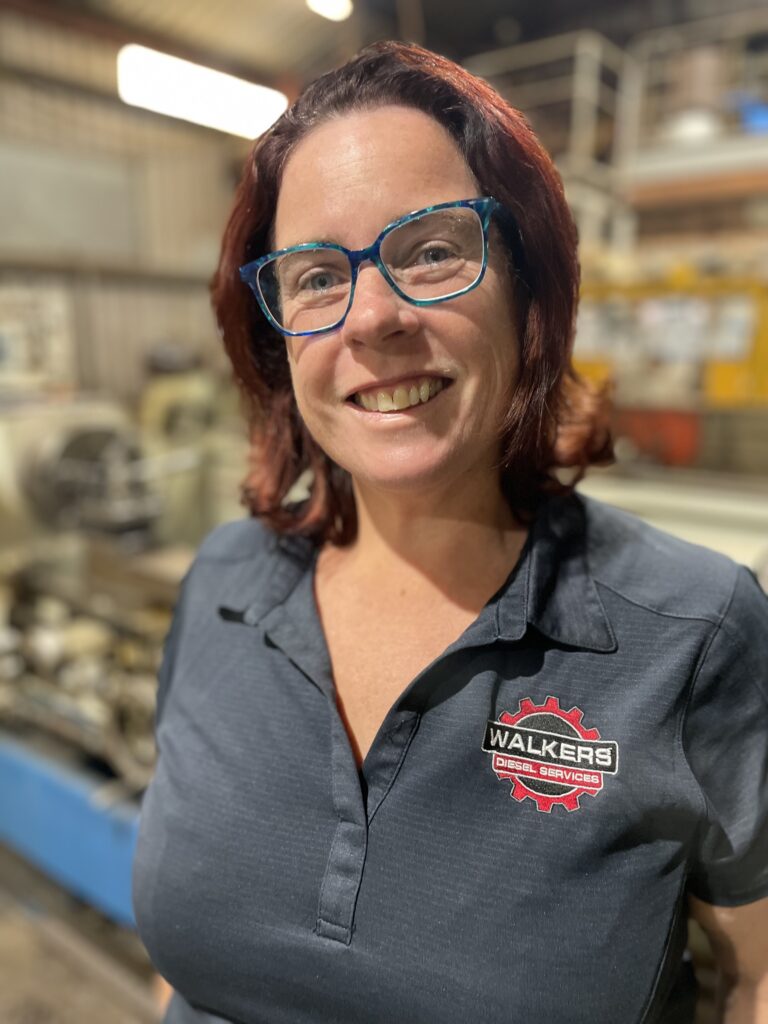

 Workforce and Leadership
Workforce and Leadership Mandy Walker is a dedicated advocate for family businesses in regional areas, recognising their pivotal role in fostering vibrant communities. Mandy’s current focus lies in developing a collaborative business model for Wheatbelt engineering enterprises to integrate into the defence industry's supply chain.
3 min read

 Rice
Rice In 2023, the AgriFutures Rice Program called for research proposals that were innovative, had the potential for transformative change for the industry, and addressed the needs and challenges of a rice industry using less water into the future. As a result, the Program has contracted a total of nine successful research proposals adding to the eighteen projects already underway.
7 min read

 Workforce and Leadership
Workforce and Leadership Nikki has been recognised for promoting the Merino wool industry through her sustainable wedding dress and special occasions brand.
3 min read

 Thoroughbred Horses
Thoroughbred Horses The opportunity to work with elite equine athletes the driving force behind Ella’s decision to apply for a Horizon Scholarship.
3 min read

 National Challenges and Opportunities
National Challenges and Opportunities More Australians than ever support the crucial work undertaken by rural industries and their significant contributions to Australian society, a new report has found.
4 min read

 Thoroughbred Horses
Thoroughbred Horses If you’re looking to develop your skills in the thoroughbred industry, then the unique experience offered through the Les Young Scholarship might be for you. Applications for the 2024 Scholarship are now open.
4 min read
Our vision is to grow the long-term prosperity of Australian rural industries. Since our inception in 1990, AgriFutures Australia, formerly RIRDC, has grown and developed alongside our 13 levied industries and we’re honoured to continue this important role in supporting the growth and overall success of Australian agriculture.
Learn more about AgriFutures Australia
The University of Sydney
6 October, 2022 - 29 April, 2026

University of the Sunshine Coast
19 September, 2022 - 19 January, 2024

Cross sector
1 January, 2022 - 31 December, 2022
